Automation is fundamentally reshaping heavy industries, including steel production and foundries. As businesses strive to enhance productivity, safety, and cost-effectiveness, adopting advanced automation technologies has become a strategic imperative. This article explores the impact of automation in these sectors and highlights the key trends and technologies driving this transformation.
Enhancing Productivity

One of the primary benefits of automation in heavy industries is the significant boost in productivity. Automation technologies, such as robotic process automation (RPA) and artificial intelligence (AI), streamline operations, reduce manual intervention, and improve production rates. For example, in steel manufacturing, automated systems can monitor and control production processes in real-time, enabling manufacturers to respond swiftly to changing conditions and optimize output .
Additionally, automation allows for better resource management, leading to reduced waste and enhanced efficiency. A study by McKinsey noted that fully automated plants can achieve productivity gains of up to 20-30% compared to traditional operations .
Improving Safety
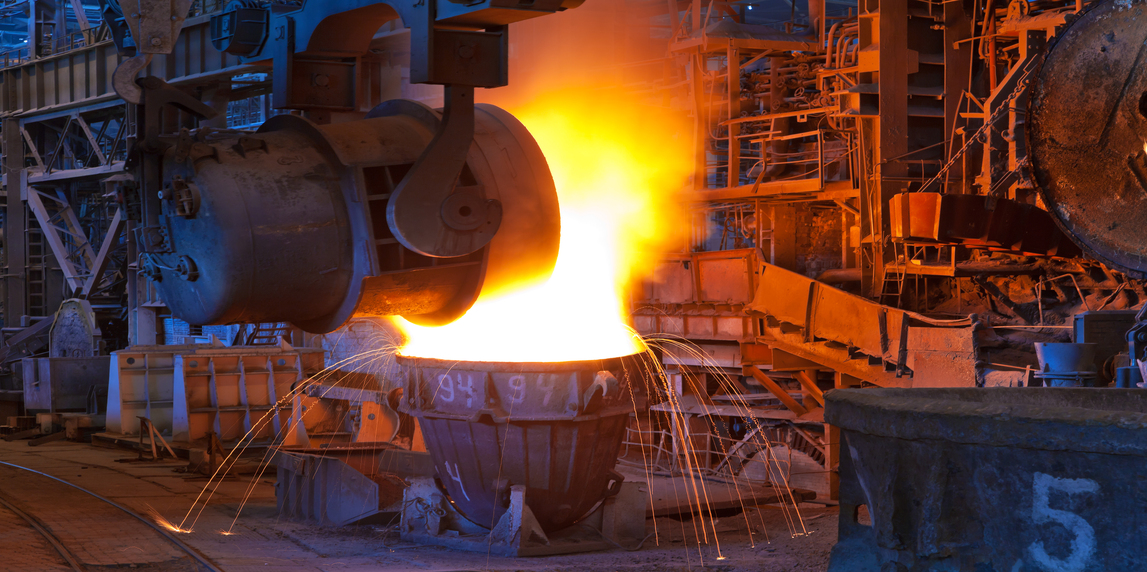
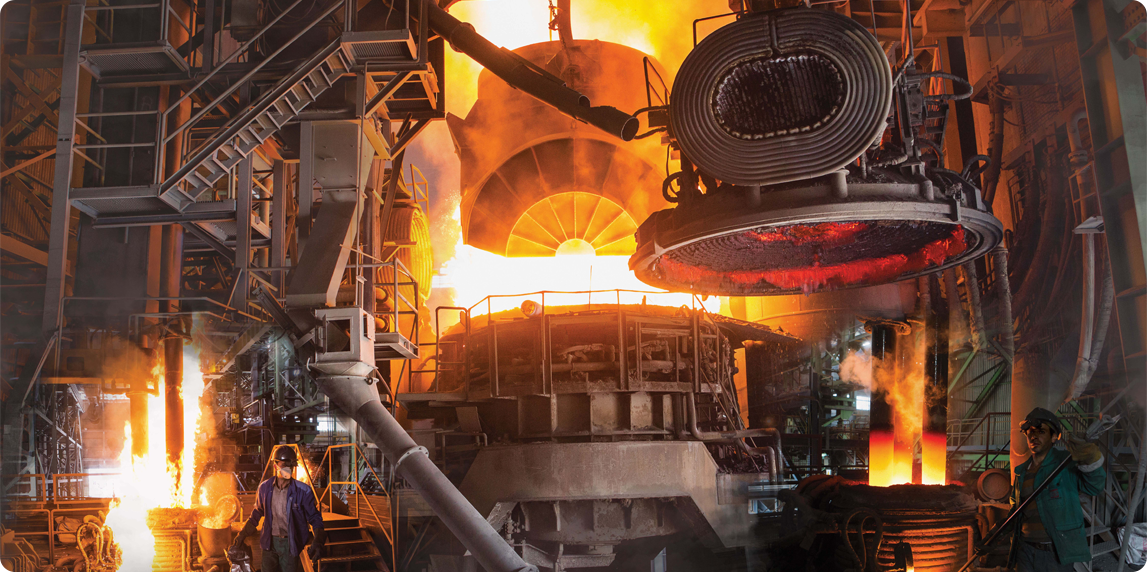
Safety is a paramount concern in heavy industries, where the risks associated with manual labor can be significant. Automation technologies mitigate these risks by replacing humans in hazardous environments. For instance, autonomous vehicles and robotic systems can perform tasks in dangerous settings, such as handling molten metal in foundries or transporting heavy materials in steel mills .

Moreover, automation systems can enhance workplace safety by implementing real-time monitoring and predictive analytics. These systems can identify potential hazards and notify workers, reducing the likelihood of accidents. A report from the World Economic Forum emphasizes that automation can lead to safer working conditions, ultimately improving employee morale and reducing liability for companies .
Cost-Effectiveness
The long-term cost savings associated with automation are significant. While the initial investment in automated technologies can be substantial, the return on investment often justifies the expense. Automation reduces labor costs by minimizing the need for manual labor, particularly in repetitive tasks. This shift allows companies to allocate their workforce to more strategic roles that require human expertise
Furthermore, automated systems contribute to lower operational costs through improved efficiency and reduced waste. According to a study by Deloitte, companies that implement automation can achieve cost reductions of up to 30% over time
Key Technologies Driving Automation
Several key technologies are driving automation in heavy industries:
Robotics
Internet of Things (IoT)
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Digital Twins
Conclusion
The impact of automation in heavy industries is profound, leading to increased productivity, improved safety, and greater cost-effectiveness. As companies adopt advanced technologies such as robotics, IoT, AI, and digital twins, they position themselves for success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Embracing these trends not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to safer and more sustainable practices in sectors like steel production and foundries. As automation continues to evolve, industries that prioritize these innovations will be better equipped to meet the challenges of the future.
- McKinsey & Company: Automation in Manufacturing
- Deloitte Insights: Automation and Productivity
- World Economic Forum: The Future of Work in Automation
- Robotics Online: The Role of Robotics in Heavy Industries
- IoT Analytics: The Impact of IoT on Manufacturing
- Forbes: The Rise of Digital Twins in Manufacturing
- Harvard Business Review: The Promise of AI in Manufacturing
lpipl
lpiplYou Might Also Like
- lpipl
- 0 Comments
- lpipl
- 0 Comments
- lpipl
- 0 Comments